Connected memory size
Since there are 24 address buses (A0 to A23), up to 16Mbytes of memory can be connected. If the memory to be connected is 1Mbyte or smaller, only 20 address buses (A0 to A19) are required and the remaining 4 pins can be used for other purposes.
Data bus width
Since the H8/300H is a 16-bit CPU, it has 16 pins (D0 to D15) for reading and writing 16-bit data. If word data is allowed to be divided into two by the MOV.W instruction, only 8 data bus pins (D8 to D15) are required and the remaining 8 pins (D0 to D7) can be used for other purposes.
As described above, the use of pins determines whether the memory address is 16M or 1M and the data bus is either 16 or 8 bits. So you have to figure out the most effective use with the limited number of pins.
Address strobe
Indicates that an address is valid and that it is external when it is at low level. It is not set at low level if an address is internal (internal ROM or RAM). When the CPU is reading or writing data from/to the internal ROM or RAM, reading/writing is not available externally. The RD, HWR and LWR signals are not changed to low level, either.
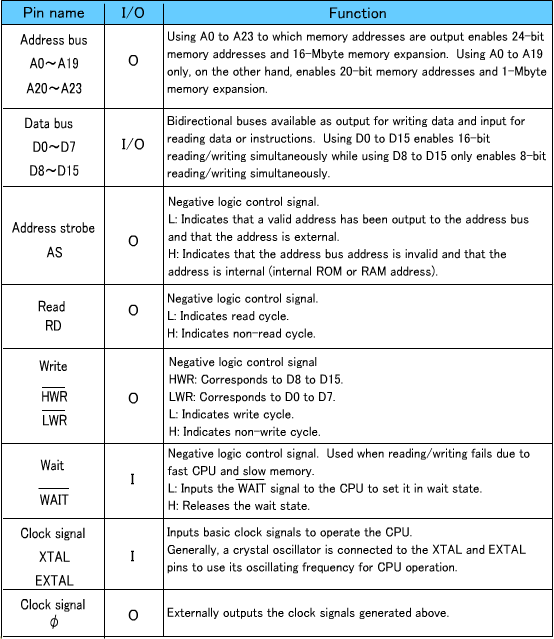
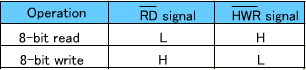
Read/write signals
When the data bus width is 8 bits (RD and HWR are used):
Data buses D8 to D15 are used, and D0 to D7 are not.
When the data bus width is 16 bits (RD, HWR and LWR are used):
|